Efficiency, reliability and uninterrupted power
The Hybrid Solar Inverter of the solarT line is very versatile, aiming to achieve maximum energy efficiency. Provides 5 functionalities in a single topology:
Ongrid and offgrid inverter;
- Ongrid inverter with offgrid function;
- UPS for specific consumers that interacts with the grid;
- Bidirectional Inverter for Battery Charge;
- Inverter with MPPT function;
- 4-wire inverter, no transformer required to generate neutral.
Product details
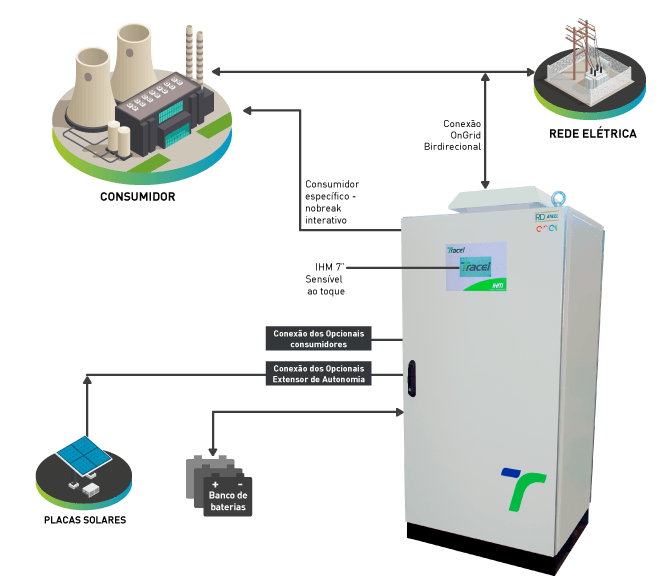
Tracel’s Hybrid Solar Industrial Inverter is ideal for supplying specific consumers when operation should be safe and uninterruptable. The system is available in the versions of 20, 30, and 50 kW.
The system has an innovative topology and is totally national. An unique inverter that combines the characteristics of ongrid, offgrid, and MPPT equipement, with bidirectional functionality for charging battery banks or supplying the grid with battery bank energy.
Not only the inverter, this system also has an electromechanical switch, an ultra-fast static transfer switch, and a load controller. All modules are enclosed in a single cabinet.
Another differential this product offers is a 4-wire inverter, P+P+P+N, no transformer is required for this function.

Operating Modes
The inverter has many operating schemes, depending on the context and electrical parameters.Operating mode options are selected according to each client’s needs through the Human-Machine Interface (IHM) with a touch-sensitive 7″ display or through a computer with Ethernet connection.
Different than other hybrid inverters sold in Brazil, this product supplies specific consumers in parallel (interactive) to the main grid. If the grid oscillates beyond the specified limits for the consumer, the inverter disconnects from the grid through the ultra-fast static transfer switch before the consumer experiences oscillations or grid power interruption. For safety reasons, when an interruption or phase fault from the grid occurs, not only is there the static transfer switch, but also a electromechanical swich that unlatches the inverter from the grid.
In normal operating conditions, during the day, photovoltaic panels supply specific consumers and mantain batteries in floating voltage. Excess energy generated from the panels is injected to the grid operator, functioning as distributed energy generation for consumer billing deductions.
In energy efficiency mode, the inverter’s priority is to consume as least energy as possible from the grid. If solar panel shadowing occurs, battery banks supply energy to specific consumers without using grid energy until there is no more shadowing or until the bank reaches its lowest operating limit.
When panel energy normalizes, the battery charging cycle starts return the battery bank to a fully charged state. In UPS mode, the priority of the inverter is to guarantee interruptible supply of energy to specific consumers. If grid interrupion occurs, the inverter disconnects specific consumers from the main grid while maintaing power from photovoltaic panels and/or battery banks.
During night operation the inverter also has energy efficiency and UPS modes. In energy efficiency mode the battery banks that are in a floating voltage state can divert energy stored throughout the day to the main grid. In UPS mode, the inverter maintains the battery bank in a floating voltage state with grid energy, and if grid oscillations or interruption occur, the inverter unlatches from the grid and supplies specific consumers according battery charge limit. When the grid returns to a normal state the inverter recharges the battery bank.
Battery bank autonomy depends on bank dimensions. When a grid energy fault occurs for a long period or if the bank is designed only for short interruptions, there is a possibility in coupling a motor generator set to the inverter providing power continuity to specific consumers.